Asynchronous Motors
Asynchronous motors are one of the most-widely used electric machines globally. With their compact and sturdy construction, asynchronous motors guarantee maximum service life and maintainability for decades. ELIN Motors globally deliver asynchronous machines according to customer specifications in various designs and performance levels, amongst others, to the following industry fields:
- Wind Energy
- Power Plant Engineering
- Mining
- Plastics Industry
- Oil and Gas Industry
- Chemical Industry
- Metal Industry
- Marine Industry
As a globally operating specialist for electric machines, ELIN Motors is your perfect partner for asynchronous motors in any design and size.
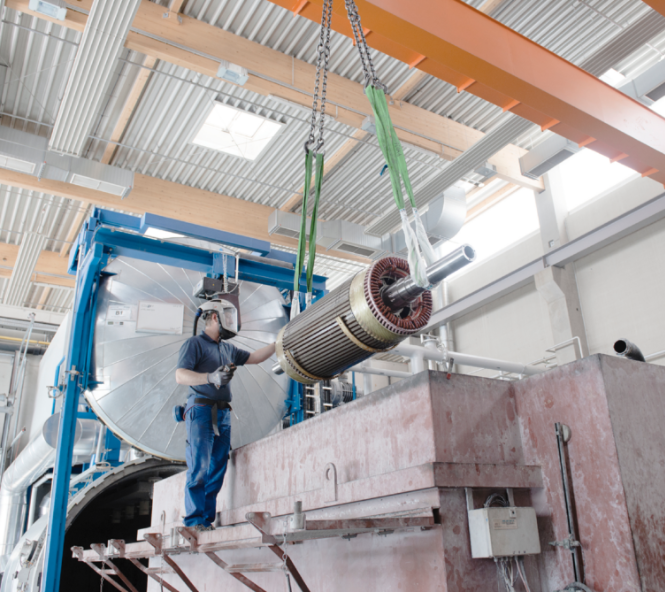

Asynchronous Motors According To Types
Asynchronous Motors by ELIN Motoren stand out due to their high levels of efficiency and reliability. Our high voltage asynchronous motors are constructible with various cooling systems (air-cooled or water-cooled) and are manufactured on the highest state-of-the-art level. Beside designs with cage rotors, slip-ring rotors are part of our product portfolio as well.
| Voltage Range: | Low Voltage | High Voltage |
| Rotor Design: | Squirrel-Cage Rotor | Slip-Ring Rotor |
| Cooling Technique: | Air Cooling | Water Cooling |
High Voltage Asynchronous Motors
High voltage asynchronous motors are mostly operated with a voltage starting at 1 kV. ELIN Motoren supplies customized high voltage asynchronous motors within a voltage range of 1 kV up to 15 kV. The implemented preformed coil winding stands out due to highest precision and the use of special materials on the highest technological level. A perfectly adapted manufacturing technology with a high degree of automatization and a technologically sophisticated pressure-impregnation technique ensure maximum service life and reliability.
Low Voltage Asynchronous Motors
Low voltage asynchronous motors are operated with a voltage of up to 1 kV. ELIN Motors supply various winding systems for these voltage ranges such as round wire winding or preformed coil winding. Also unique windings for special voltage can be achieved. Automated manufacturing steps and methods allow highly efficient and shortest possible production runs. Perfectly coordinated materials and impregnation techniques ensure maximum service life and reliability. If rendered necessary for special frequency converter applications, according materials and manufacturing processes are implemented.
Squirrel-Cage Rotor (Cage Rotor)
The squirrel-cage rotor, also referred to as cage rotor, is the simplest form of an asynchronous machine. The rotor body consists of a stack of laminated iron sheets in which slots are punched into the circumference. In these slots, copper bars are inserted which on both ends are short-circuited with a copper ring. However, not only copper is used as a conductor material in a cage rotor. For very small machines, the entire cage is cast via centrifugal casting out of aluminium. Machines with unique starting requirements also demand materials with adapted conductivity such as bronze.
Slip-Ring Rotor
In design with a slip-ring rotor, the rotor carries a three-phase winding with the same pole number as the stator. The winding wired in delta or star connection is led out on the ends via three slip-ring contacts. These can either be connected to starting resistance or, in case of DFIG, to a converter.
Motor Details
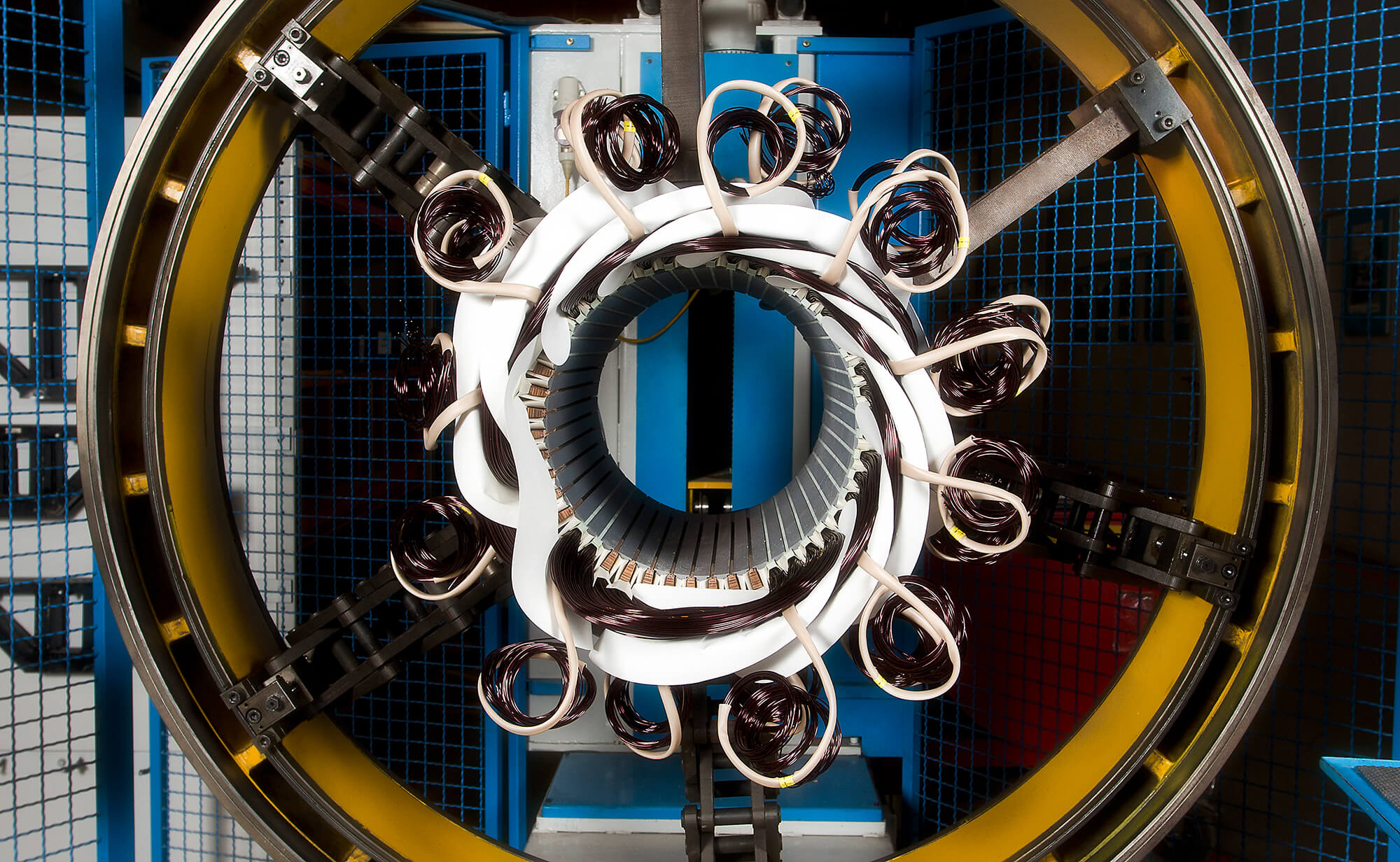
The operating principle of any electric machine is defined by the reciprocal repelling of the magnetic fields of stator and rotor. In case of the asynchronous machine, the stator rotating field is produced by the three-phase winding in the stator. As the rotor only consists of a short-circuited winding, an electric current in the rotor winding must be generated by induction in order to create a field which repels the stator. The principle of induction, however, only succeeds if the stator rotating field and the rotor cage run asynchronously. Conversely, the machine cannot develop torque in synchronism.
The most vital components of asynchronous motors are:
- Active parts (stator / rotor)
- Casing
- Shaft
- Bearing shield
- Bearing
- Fan
- Terminal box, auxiliary terminal box
- Sensor system (temperature, vibrations, etc.)
- Stand-by heating (optional)
- Additional equipment according to customer requirements
Cooling Systems Of Electric Motors
In general, primary coolants for asynchronous motors are air and water. Only the machine’s cooling system ensures the operating point in the required heating phase. Within the defined heating phases, one and the same active part (stator + rotor body) can release more power on the shaft if cooled via air-water heat exchanger than via air-air heat exchanger.
In the following you can find an example of the applied cooling systems:
| IC411 | Surface Cooling (heat derivation via fins and ribs on casing) – airflow is provided by a fan on second shaft end. |
| IC81W | Air-Water Heat Exchanger |
| IC511 | Recooling via air-air heat exchanger (pipe machine) |
| IC611 | Recooling via air-air heat exchanger (external-fitting) |
| IC7A0W7 | Water-Jacket Cooling |
| IC01 | Open Construction: cooling via ambient air |
Hybrid cooling techniques as customized solutions are realized by ELIN Motoren just as well as submerged propulsions up to an immersion depth of 100 metres.
Types Of Motors
You are looking for asynchronous motors for industry applications? Send us your inquiry!